
This book compiles the state of knowledge of this rapidly evolving field, and presents an integrated approach that includes technology, management and planning. It addresses the planning and organization of the entire faecal sludge management service chain, from the collection and transport of sludge and treatment options, to the final enduse or disposal of treated sludge. In addition to providing fundamentals and an overview of technologies, the book goes into details of operational, institutional and financial aspects, and provides guidance on how to plan a city-level faecal sludge management project with the involvement of all the stakeholders.
To know more: www.sandec.ch/fsm_book

This document is a comprehensive and user-friendly capacity development tool for sanitation solutions in emergency settings. It provides detailed information on key decision criteria for tried and tested emergency sanitation technologies and information on cross-cutting issues such as inclusive design, soil analysis and institutional framework, relevant to come up with informed sanitation technology decisions in emergencies.
www.emersan-compendium.org

Double vault Urine Diversion Dry Toilets (UDDT) can be used as an alternative to pit latrines in refugee camps. They utilise two chambers for faeces, one of which is in use whilst the other is full and drying so that it can be safely disposed of after an appropriate period of time.
These Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs) were developed by Oxfam under UNHCR’s “Waste to Value” Project, which was funded by the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation. They are largely based on UDDTs developed under the Waste to Value Project in Ethiopia.

This document contains documentation to help UNHCR and WASH actors build pour flush institutional latrines in refugee settings with septic tanks and drain fields. The package includes: Technical Drawings; Step by Step Construction Drawings; Bills of Quantity; Material and Workmanship Specifications; and Design Calculations.
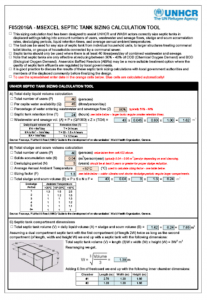
This sizing calculation tool has been designed to assist UNHCR and WASH actors correctly size septic tanks in displaced settings taking into account numbers of users, wastewater and sewage flows, sludge and scum accumulation rates, desludging periods, liquid retention times, and average annual ambient temperatures.

The book Emergency Sanitation: Assessment and programme design has been produced to assist those involved in planning and implementing emergency sanitation programmes. The main focus of the book is a systematic and structured approach to assessment and programme design. It provides a balance between the hardware (technical) and software (socio-cultural, institutional) aspects of sanitation programmes, and links short-term emergency response to long-term sustainability. The book is relevant to a wide range of emergency situations, including both natural and conflict-induced disasters, and open and closed settings. It is suitable for field technicians, engineers and hygiene promoters, as well as staff at agency headquarters.

The purpose of the manual is to provide practical guidance on how to select, design, construct and maintain appropriate excreta disposal systems in emergency situations. Relevant situations include natural disasters, relief for refugees and Internally Displaced Persons (IDPs), and complex emergencies, focusing on rural and peri-urban areas. The manual presents a process, which can be followed to assess the current excreta disposal needs and priorities, and to design an appropriate programme to respond to those needs. It can also be used to select appropriate excreta disposal technologies, systems, and hygiene promotion interventions. The manual provides guidance on how to plan, design and construct systems, and how to maintain and promote appropriate use of those systems.
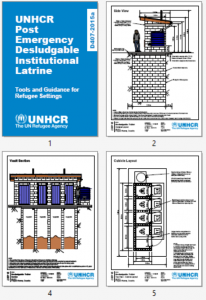
This document contains documentation to help UNHCR and WASH actors build desludgable institutional latrines in refugee settings. The package includes: Technical Drawings; Step by Step Construction Drawings; Bills of Quantity; Material and Workmanship Specifications; and Design Calculations.

This document contains guidelines for toilets in refugee settings including: site selection; prevention of surface or ground water contamination; pit reinforcement; toilet slab strength; toilet slab anchorage; sanitary sealing; use of plastic sheeting; toilet doors; privacy walls; vector control measures; rain and stormwater protection; wash block accessories; collection of anal cleansing and sanitary materials; material specifications; handwashing stations design considerations; and environmental considerations for sourcing wood .
Tags: Communal Toilets, Communal Toilets, Communal Toilets, Communal Toilets, Communal Toilets, Communal Toilets, Communal Toilets, Household Toilets, Household Toilets, Household Toilets, Household Toilets, Household Toilets, WASH Programme Management, WASH Programme Management, and WASH Strategy Development. Categories: WASH Design Guidelines, WASH Design Guidelines, WASH Design Guidelines, WASH Guidelines, WASH Guidelines, WASH Policy Guidelines, WASH Technical Designs, WASH Technical Designs, WASH Technical Designs, WASH Technical Designs, and WASH Technical Designs.

The choice of sanitation technology in humanitarian crisis is based on various factors including the terrain, social and cultural norms and agency experience. There is the continued need for humanitarian response mechanisms to factor the environmental impact and sustainability of the technologies used in the provision of safe water supply and sanitation to affected communities. The acceptability of using ecological sanitation technologies such as Urine Diversion Dry Toilets (UDDT) in refugee contexts needs significant exploration. Using refugee camps in Dollo Ado as a case study, this paper outlines how the UDDT technology has been implemented in the context of protracted refugee camps, the successes and the areas needing further exploration to make it better able to be adopted across various refugee programmes and contexts.
Tags: Excreta / Urine ReUse, Excreta / Urine ReUse, Excreta / Urine ReUse, Excreta / Urine ReUse, Excreta / Urine ReUse, Excreta Composting, Excreta Composting, Excreta Composting, Excreta Composting, Excreta Composting, Excreta Management, Excreta Management, Excreta Management, Excreta Management, Excreta Management, Excreta Management, Excreta Management, Excreta Management, Excreta Management, and Excreta Management. Locations: Africa, Dollo Ado, East and Horn of Africa, Ethiopia, and Ethiopia. Languages: English, English, English, English, English, English, English, English, English, and English. Organisations: CDC, OXFAM GB, OXFAM GB, UNHCR, UNHCR, UNHCR, UNHCR, UNHCR, UNHCR, WEDC, WEDC, and WEDC. Categories: WASH Reference Documents, WASH Reference Documents, WASH Reference Documents, WASH Reference Documents, WASH Reference Documents, WASH Reference Documents, WASH Reference Documents, WASH Reference Documents, WASH Reference Documents, WASH Reference Documents, and WASH Research Documents.










