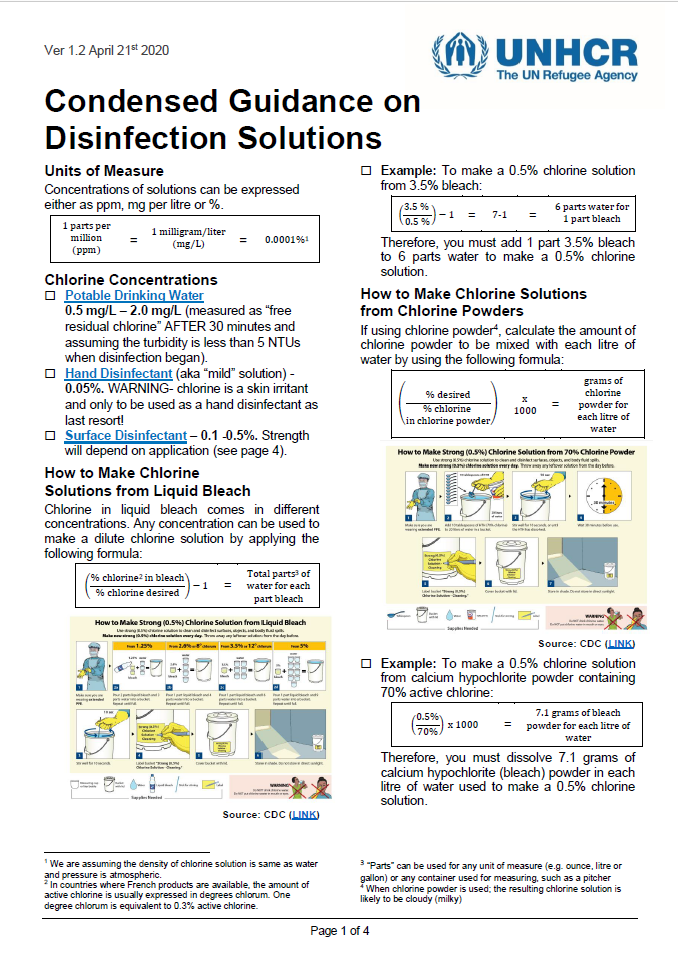
This condensed guidance note has been written to summarize the various low and intermediate strength disinfectants, their uses, advantages and disadvantages, and how to formulate them using various chlorine compounds.
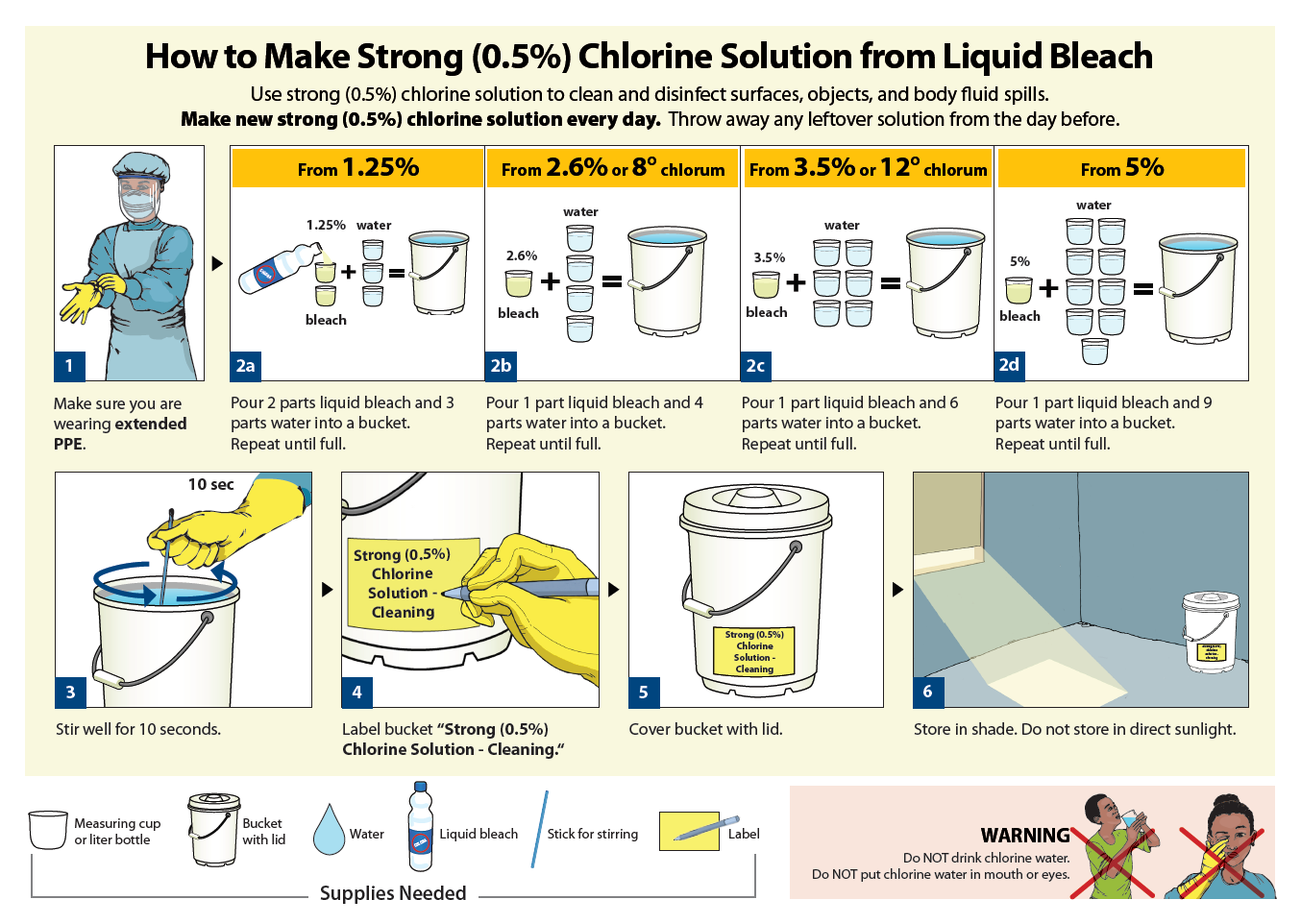
This simple poster describes how to make a simple strong chlorine solution of 0.5% using bleach for disinfection in healthcare facilities and public latrines.
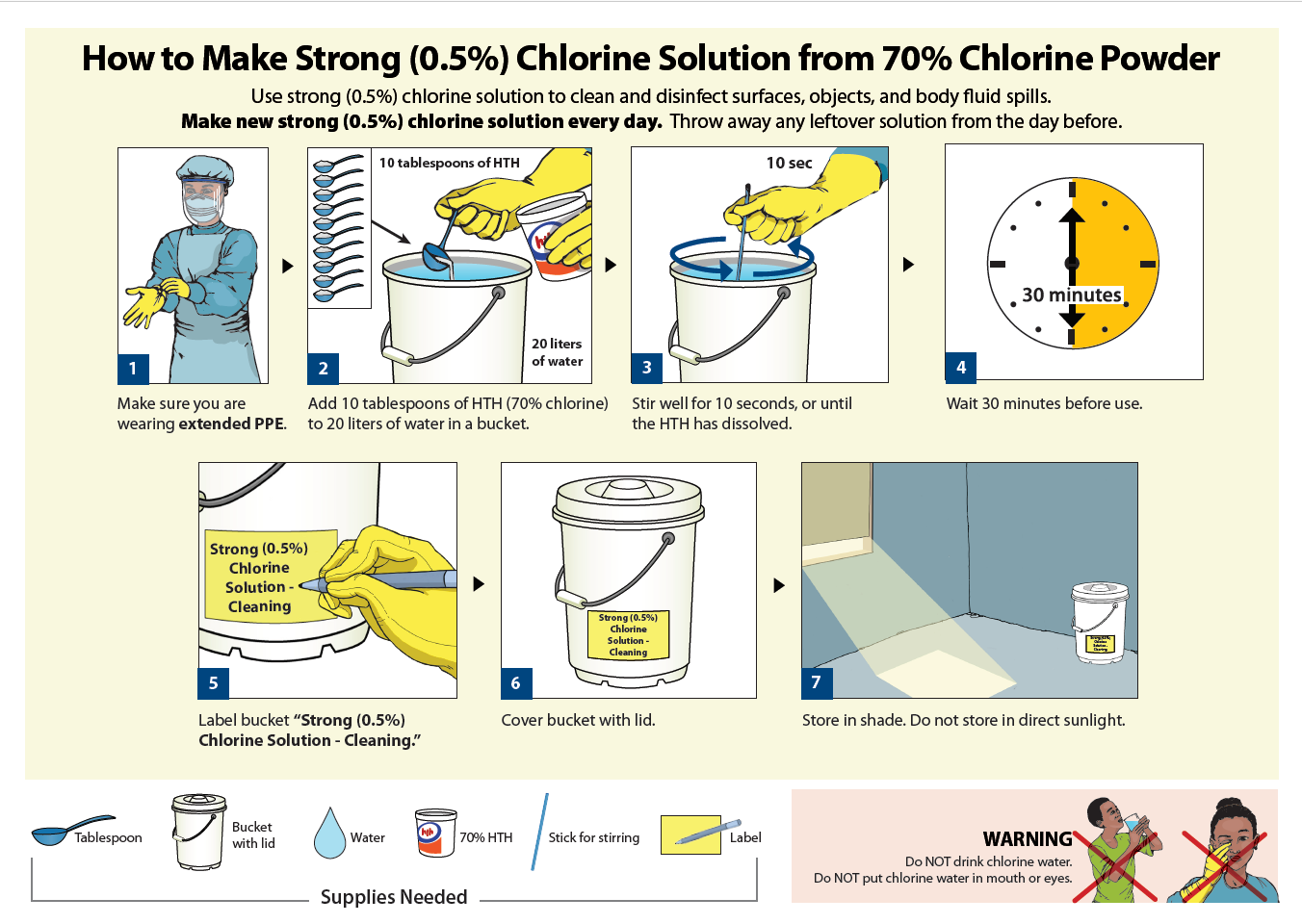
This simple poster describes how to make a simple strong chlorine solution of 0.5% using chlorine powder for disinfection in healthcare facilities and public latrines.
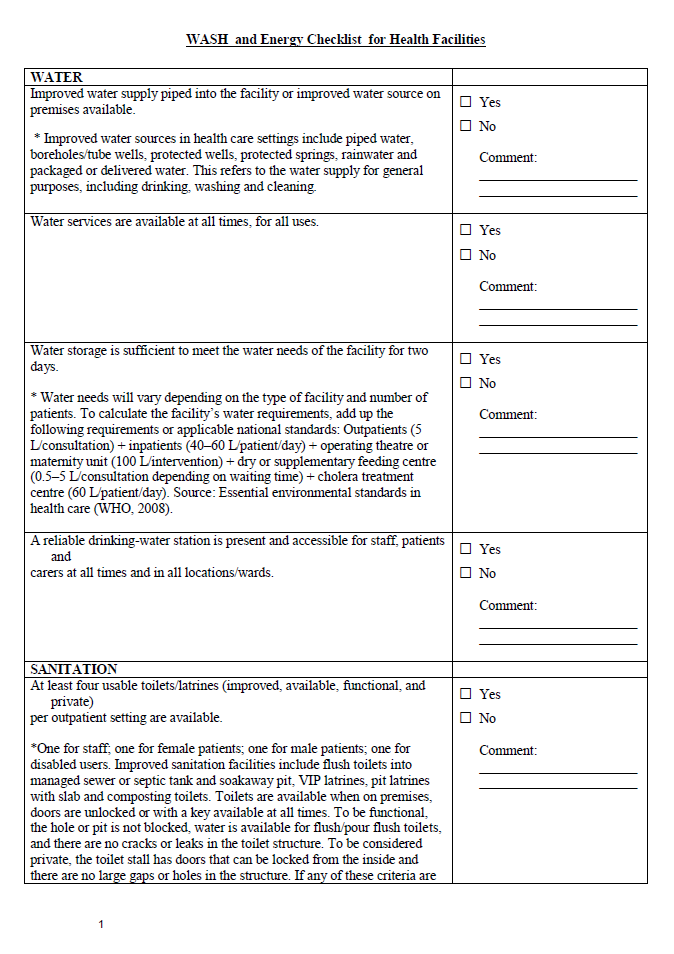
A WASH and Energy Checklist for rapid assessments of Health Facilities in refugee contexts.

WASH FIT is a risk-based, continuous improvement framework with a set of tools for undertaking water, sanitation and hygiene (WASH) improvements as part of wider quality improvements in health care facilities. It is aimed at small primary, and in some instances secondary, health care facilities in low and middle income countries. WASH FIT is an adaptation of the water safety plan (WSP) approach, which is recommended in the WHO Guidelines for Drinking-water Quality as the most effective way of ensuring continuous provision of safe drinking-water. It is aimed at small primary, and in some instances secondary, health care facilities in low and middle income countries.

This document provides an overview of specific health care waste technologies for the treatment of solid infectious and sharp waste. For each technology, details of its operation, effects on the environment and health, requirements for installation, capacities for treating waste, examples of consumables and advantages and disadvantages are described. The document is designed for health care facility administrators and planners, WASH and infection prevention control staff, national planners, donors and partners.

This handbook provides comprehensive guidance on safe, efficient, and environmentally sound methods for the handling and disposal of health-care wastes in normal situations and emergencies.

This document contains recommendations for setting minimum Water, Sanitation and Hygiene (WASH) standards in health-care facilities in emergencies in order to provide an adequate and safe level of health-care in addition to minimizing the risk of health-care facility related infection for patients, staff and carers.

This document provides guidance on essential environmental health standards required for health care in medium- and low-resource countries and support the development and implementation of national policies. These guidelines have been written for use by health managers and planners, architects, urban planners, water and sanitation staff, clinical and nursing staff, carers and other health-care providers, and health promoters.
Tags: Cross Cutting, Cross Cutting, Drainage, Drainage, Drainage, Excreta Management, Excreta Management, Excreta Management, Hygiene Promotion, Hygiene Promotion, Hygiene Promotion, Medical Waste Management, Medical Waste Management, Medical Waste Management, Medical Waste Management, Medical Waste Management, Public Health, Public Health, Public Health, Public Health, Public Health, Public Health, Public Health, Public Health, Public Health, Solid Waste Management, Solid Waste Management, Solid Waste Management, Water Supply, Water Supply, and Water Supply. Languages: English, English, English, English, English, English, English, English, and English. Organisations: WHO, WHO, WHO, WHO, and WHO. Categories: WASH Indicators and Standards, WASH Indicators and Standards, WASH Policy Guidelines, WASH Policy Guidelines, WASH Reference Documents, WASH Reference Documents, WASH Reference Documents, WASH Reference Documents, WASH Reference Documents, WASH Reference Documents, WASH Reference Documents, WASH Reference Documents, and WASH Reference Documents.









