
This document looks at drinking water, sanitation and renewable energy solutions and options in three camps in Dolo Odo with recommendations and conclusions.

The choice of sanitation technology in humanitarian crisis is based on various factors including the terrain, social and cultural norms and agency experience. There is the continued need for humanitarian response mechanisms to factor the environmental impact and sustainability of the technologies used in the provision of safe water supply and sanitation to affected communities. The acceptability of using ecological sanitation technologies such as Urine Diversion Dry Toilets (UDDT) in refugee contexts needs significant exploration. Using refugee camps in Dollo Ado as a case study, this paper outlines how the UDDT technology has been implemented in the context of protracted refugee camps, the successes and the areas needing further exploration to make it better able to be adopted across various refugee programmes and contexts.

Current emergency safe water guidelines are based on little field evidence. We launched an observational study on chlorine decay in the Azraq refugee camp, Jordan in July-August 2014 in order to: i) develop evidence-based guidelines for centralized batch chlorination in humanitarian operations; and ii) identify factors affecting the safe water chain. This study builds on earlier work from South Sudan and adds to the evidence base that study initiated.

Close to half a million refugees live in Dadaab, Kenya and rely on groundwater from the Merti Aquifer. Preliminary hydrogeological mapping indicates over exploitation of the fresh water aquifer could result in salt water intrusion, which would put the security of water supply for the refugee camps and host population at risk. UNHCR together with University of Neuchâtel has embarked on a comprehensive study of the Merti Aquifer including remote monitoring, and numerical modelling of the aquifer in order to develop a sustainable groundwater management plan for the aquifer which supplies water to all the refugee camps in Dadaab, Kenya.

Water safety plan produced by CDC following a technical support visit to Dadaab in 2009. The report contains: An overview of Dadaab water supply system; Identification of hazards and risks; Control measures and prioritisation of risks; Sanitation and hygiene; and Conclusions.

This brief is intended to highlight key WASH elements for camps closure. It focuses on specific actions, including the highlights of public health risks associated with health, water, sanitation, and hygiene (WASH) when dealing with decommissioning of WASH infrastructures. The overall closure implementation actions and modus operandi should be context specific and properly planned in coordination with key stakeholders.
Tags: Camp Closure, Cross Cutting, Environment, Excreta Management, Solid Waste Management, WASH Coordination, WASH Programme Health and Safety, WASH Programme Management, WASH Strategy Development, and Water Supply. Languages: English. Organisations: UNHCR. Categories: WASH Guidelines, WASH Operational Guidelines, WASH Policy Guidelines, and WASH Reference Documents.

The report examines the feasibility of a wide range of standard sanitation technologies in addition to sanitation innovations in refugee contexts (including miniaturized biogas, reinvented toilets, new processor technologies, SMS dispatching, pay per use toilets, sale of by-products). Technologies were evaluated based on upfront investment cost; technology viability, suitable size and transportability; flexibility and resilience; and value for money.

This report presents a methodology to cost water services that has been adapted from the life-cycle costs approach (LCCA) and looks at its applicability to refugee settings.
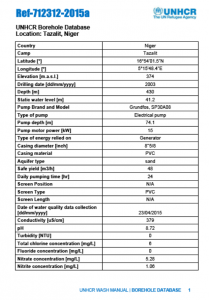
Tazalit Country Niger Camp Tazalit Latitude [°] 16°54’01.5″N Longitude [°] 5°15’48.4″E Elevation [m.a.s.l.] 374 Drilling date [dd/mm/yyyy] 2003 Depth [m] 430 Static water level [m] 41.2 Pump Brand and Model Grundfos, SP30A08 Type of pump Electrical pump Pump depth [m] 74.1 Pump motor power [kW] 15 Type of energy relied on Generator Casing diameter [inch] […]
Tags: Boreholes, Drilling, and Water Supply. Locations: Africa, Niger, and West Africa. Languages: English. Organisations: UNHCR. DatabaseDocTypes: Borehole Drilling Logs.

These WASH related primer questions have been designed to assist UNHCR and WASH actors collect data from key informants and focus groups during WASH assessments. The list of questions is not exhaustive and is merely intended as a conversation primer (aide memoire).
Tags: Excreta Management, Human Right to Water / Sanitation, Hygiene Promotion, Protection, Public Health, Solid Waste Management, WASH Assessments, WASH Monitoring, WASH Strategy Development, and Water Supply. Languages: English. Organisations: UNHCR. Categories: WASH Blank Forms, WASH Emergency Guidelines, WASH Emergency Tools, and WASH Reference Documents.
 English
English










