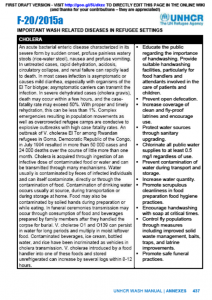
This document provides a quick summary of the most important WASH related diseases for refugee settings and includes a list of recommended control strategies.

This document describes UNHCR’s global strategy for public health through a set of guiding principles and strategic approaches including protection; age, gender and diversity; equity; access; sustainability; community empowerment; appropriateness and reliability; partnerships and coordination; capacity building; communication and advocacy; integrated approaches; measurement and monitoring; and innovation. The document describes strategic objectives and enabling actions per sub-sector (Public Health, HIV and Reproductive Health, Food Security and Nutrition, and WASH).
Tags: Capacity Building, Disease Vector Control, Excreta Management, Gender, Gender Based Violence, Human Right to Water / Sanitation, Hygiene Promotion, Protection, Public Health, Value for Money, WASH Coordination, WASH Monitoring, WASH Strategy Development, and Water Supply. Languages: English. Organisations: UNHCR. Categories: WASH Guidelines, WASH Operational Guidelines, WASH Policy Guidelines, and WASH Reference Documents.

This technical brief is intended to provide guidance for UNHCR staff and Partners involved in winterization of WASH facilities in the current European refugee and migrant situation.
Tags: Bathing Facilities, Cold Climates, Cross Cutting, Excreta Management, Hygiene Promotion, Piped Water Networks, and Water Supply. Locations: Central Europe and the Baltic States, Eastern Europe, and Europe. Languages: English. Organisations: UNHCR. Categories: WASH Emergency Guidelines, WASH Emergency Tools, WASH Guidelines, WASH Operational Guidelines, WASH Policy Guidelines, and WASH Reference Documents.

This document provides health and safety guidelines for refugee WASH programmes for staff are involved in either: cleaning of toilets; maintenance of toilets; desludging of toilets; the collection and movement of excreta; the collection or movement of solid wastes; the handling of vector control or water treatment chemicals; any staff who may potentially come into contact with excreta, sewage, wastewater, solid waste, medical waste or any other sources of (potential) infection.

This document contains guidelines for toilets in refugee settings including: site selection; prevention of surface or ground water contamination; pit reinforcement; toilet slab strength; toilet slab anchorage; sanitary sealing; use of plastic sheeting; toilet doors; privacy walls; vector control measures; rain and stormwater protection; wash block accessories; collection of anal cleansing and sanitary materials; material specifications; handwashing stations design considerations; and environmental considerations for sourcing wood .

This document contains guidelines to help UNHCR and WASH actors design piped water networks in refugee settings. It describes the minimum documentation that should be included for a water network design project.
Tags: Piped Water Networks, WASH Monitoring, WASH Programme Management, WASH Strategy Development, Water Pumping, Water Storage, and Water Supply. Languages: English. Organisations: UNHCR. Categories: WASH Design Guidelines, WASH Guidelines, WASH Policy Guidelines, WASH Reference Documents, and WASH Technical Designs.

This document contains guidelines to help WASH actors in refugee settings select household water treatment products. The document includes an overview of: • Categories of HWTS; • Health benefits; • When to use HWTS and existing decision tree; • Criteria regarding HWT to be considered by the field; • Mandatory components; • UNHCR Checklist for HWTS; • HWT concerns; • Household water treatment cards; • Safe water storage;• Further reading; • Acknowledgement

This brief is intended to highlight key elements of an effective response to an outbreak of hepatitis E virus (HEV) infection in refugee setting. It focuses on specific response actions, including the review of common risks associated with health, water, sanitation, and hygiene (WASH). The overall implementation of response actions and mode of operation should be context specific, as highlighted by the examples given from Dadaab (Ifo) Kenya and South Sudan.
Tags: Bulk Water Treatment, Excreta Management, Handwashing with Soap, Household Water Treatment, Hygiene Promotion, Public Health, Water Quality Testing and Surveillance, and Water Safety Plans. Locations: Africa, Dadaab, East and Horn of Africa, Kenya, South Sudan, and Sudan and Chad Special Operational Region. Languages: English. Organisations: UNHCR. Categories: WASH Emergency Guidelines, WASH Guidelines, WASH Operational Guidelines, WASH Policy Guidelines, and WASH Reference Documents.

This brief is intended to highlight key WASH elements for camps closure. It focuses on specific actions, including the highlights of public health risks associated with health, water, sanitation, and hygiene (WASH) when dealing with decommissioning of WASH infrastructures. The overall closure implementation actions and modus operandi should be context specific and properly planned in coordination with key stakeholders.
Tags: Camp Closure, Cross Cutting, Environment, Excreta Management, Solid Waste Management, WASH Coordination, WASH Programme Health and Safety, WASH Programme Management, WASH Strategy Development, and Water Supply. Languages: English. Organisations: UNHCR. Categories: WASH Guidelines, WASH Operational Guidelines, WASH Policy Guidelines, and WASH Reference Documents.
 English
English









