The Operational Support and Management chapter is available for download in PDF format in English and in French.
Operational Support and Management
EXECUTIVE DIRECTION AND MANAGEMENT (EDM)
The Executive Office formulates policies, ensures effective management and accountability, and oversees UNHCR’s activities worldwide. Its main role is to craft a clear and consistent corporate vision, operational priorities and strategies in consultation with senior management. It engages directly with donors and States at a high level to secure political and financial support for UNHCR.
The Executive Office comprises the High Commissioner, the Deputy High Commissioner, the Assistant High Commissioner for Operations, the Assistant High Commissioner for Protection and the Chef de Cabinet, and their staff. The Inspector General’s Office, the Ethics Office, the Policy Development and Evaluation Service, and UNHCR’s Liaison Office in New York report directly to the High Commissioner and work in close consultation with the Chef de Cabinet, as do the High Commissioner’s Spokesperson and the Secretary of the Executive Committee.
The Deputy High Commissioner (DHC) oversees and provides strategic leadership for all functions related to the managerial, financial, and administrative running of the Office. At the request of the High Commissioner, the DHC also leads the Innovation Unit and supervises the Solutions Steering Group. The Controller and Director of the Division of Financial and Administrative Management, as well as the Directors of the Divisions of External Relations, Human Resources Management, and Information Systems and Telecommunications all report directly to the DHC, who also supervises the Heads of the Legal Affairs Service and the Organizational Development and Management Service, as well as the Ombudsman.
The Assistant High Commissioner for Operations (AHC-O) oversees and ensures strategic leadership and direction for all UNHCR operations in the field, the five Regional Bureaux, as well as the Headquarters divisions that provide operational support in programming, emergencies, security, and supply management (DPSM and DESS).
The role of the Assistant High Commissioner for Protection (AHC-P) is to ensure that a protection focus is instilled into all aspects of UNHCR’s work, to oversee the development and implementation of protection policy and legal standards, and to engage in and coordinate high-level advocacy on protection matters. The AHC-P oversees the activities of the Division of International Protection; provides functional guidance, in particular to the Regional Bureaux, the Division of Programme Support and Management and the Division of External Relations, on protection policy and communications relating to protection; and works closely with the AHC-O to provide overall strategic direction for operations.
The Inspector General’s Office (IGO) supports the effective, efficient and accountable management of UNHCR operations, including through preventive and pre-emptive measures that minimize the need for remedial action; and upholds an environment of integrity in UNHCR by contributing to the maintenance of the highest standards of personal and professional conduct by staff. The IGO also participates in the development of relevant UNHCR policies and monitors their implementation and impact through its inspection, investigation and ad hoc inquiry activities.
The Policy Development and Evaluation Service (PDES) pursues an integrated programme focusing primarily on evaluations, but including also research, publications and academic outreach on policy issues, programmes, projects, practices and partnerships of concern to UNHCR. It aims to ensure the highest possible evaluation standards and the effective incorporation of its findings and recommendations into policy-making, planning and programming procedures to maximize the efficiency and impact of the Office’s operational activities. PDES is committed to a high degree of transparency, and ensures that all evaluation reports and policy documents prepared by or for PDES are placed in the public domain.
The Liaison Office in New York (LONY) represents UNHCR at the UN Secretariat Headquarters in New York by promoting the organization’s policies, global strategic priorities and field-based best practices. LONY promotes the needs of people of concern to the High Commissioner through active participation in dedicated fora on the maintenance of international peace and security, humanitarian reform and financing, protection of civilians, human rights mainstreaming, and sustainable development, as well as other relevant New York-led inter-agency initiatives. LONY contributes to the formulation of resolutions by the General Assembly and its subsidiary bodies, as well as the Security Council – as they pertain to people of concern – and regularly provides input to reports of the Secretary-General and other strategic reviews. Through its collaboration with NGO partners, key UN secretariat entities, and agencies, funds and programmes headquartered in New York, LONY provides strategic advice to the High Commissioner on evolving political and policy matters, and keeps UNHCR Headquarters and the Field fully abreast and engaged on developments unfolding in New York.
The Ethics Office ensures that all staff members, including affiliated work forces, understand, observe and perform their functions in line with the highest standards of integrity, and fosters a culture of respect, transparency and accountability throughout the organization as required by the UN Charter, the UNHCR Code of Conduct, and staff rules and regulations. It is responsible for setting and developing ethical standards in collaboration with the UN Ethics Office and the UN Ethics Panel, for promoting and disseminating ethics-related policies and for providing guidance to staff members and senior management on ethical standards and dilemma in order to address and prevent problems before they emerge. It coordinates and provides support in the annual delivery of refresher courses on the Code of Conduct to UNHCR operations worldwide. It is also mandated to oversee the policy on protection from retaliation for individuals who report misconduct or who participate in audits, inspections, investigations, inquiries or in the work of the Ombudsman. The Office also administers the Financial Disclosure Programme, which is designed to promote public confidence by using corporate governance best practices of transparency and disclosure.
The Organizational Development and Management Service (ODMS) maintains a strategic overview of UNHCR’s system of management and organizational design through structural and staffing reviews. The outcomes of such reviews also inform policy on organization-wide subjects, including coordination models and accountability. In addition, ODMS, where required, provides support and follow-up to audit findings and recommendations in relation to overall management structures and staffing.
The Legal Affairs Service (LAS) is UNHCR’s central legal office on non-refugee law matters and is responsible for planning, coordinating and managing the organization’s legal affairs. LAS prepares legal arrangements and provides advice on various legal aspects of UNHCR’s operations and activities, including on issues of international public law; agreements regulating UNHCR’s relations with hosting countries and other entities such as non-governmental organizations; procurement and commercial contracts; and claims and disputes involving the organization’s operational activities. It also advises on legal aspects of public and private-sector fundraising. LAS works to reduce potential financial and other types of loss through legalrisk analysis, and protects the interests of the organization in internal administration of justice proceedings. In addition to advising on organizational policies and procedures, LAS contributes to ensuring that UNHCR’s activities are carried out in accordance with its internal regulatory framework and relevant law.
The Ombudsman’s Office provides a confidential, impartial and independent service for the informal resolution of work-related problems and conflicts. The Ombudsman’s Office offers an informal alternative to formal complaint-handling systems within UNHCR, such as the Inspector General’s Office and the Joint Appeals Board. Recourse to the Ombudsman is voluntary and strictly confidential. As an informal resource, the Ombudsman does not report interaction with individuals in the organization and keeps no formal records. Wherever possible, the Ombudsman helps individuals to develop new ways to solve problems themselves and works primarily through negotiation, influence, personal powers of persuasion and good practice. The Ombudsman provides feedback to management and staff on trends, issues, policies and practices, without breaching confidentiality or anonymity. S/he also identifies emerging problems, recommends preventive measures and provides support for responsible systems change, in all cases suggesting actions or policies that will be fair, just and equitable to all parties.
Reporting directly to the Deputy High Commissioner, the Enterprise Risk Management (ERM) unit supports organization-wide risk management at all levels of the organization. The unit is complemented by a network of risk management focal points across the organization to decentralize competence and capacity for risk management in the Field and at Headquarters.
DIVISION OF EXTERNAL RELATIONS (DER)
The Division of External Relations (DER) mobilizes public, political, financial and operational support for UNHCR’s activities around the globe. DER carries out advocacy, awareness-raising and communications activities, including through a new digital engagement strategy, and dedicated communications strategies for emergencies and crises. DER also supports UNHCR’s governing bodies and manages strategic relations with various partners from the private sector, non-governmental organizations, civil society and the UN system.
The Communications and Public Information Service (CPIS) is responsible for the production of multimedia content and relations with global media, including reputation management, political support and advocacy. CPIS generates media and multimedia events; manages the online and news activities of the organization; and undertakes global media placement and roll-out for all of UNHCR’s major communications campaigns. In addition, it provides coordination, communications advice and other support to the Field.
The Digital Engagement Section works to increase overall digital engagement with online communities and audiences, and ensures that timely and relevant digital communications are in place. The overall goal is to generate greater awareness and engagement through digital content and campaigns, building a strong voice for UNHCR on digital platforms.
The Strategic Communications Section was established in 2013 to develop an integrated global strategic communications framework for UNHCR. The Section works to align and coordinate communication on core advocacy issues, and ensures coherent strategies and branding across the organization.
The Events, Campaigns and Goodwill Ambassador Section brings greater media attention to UNHCR through coordinated campaigns and events, using the World Refugee Day campaign as a key moment to put the issue of forced displacement on the public agenda. The Section also works to further elevate the status of UNHCR’s Nansen Refugee Award and expand the Goodwill Ambassador programme to reinforce and amplify UNHCR’s messaging, events and campaigns, as well as key funding appeals and emergency operations.
The Donor Relations and Resource Mobilization Service (DRRM) is responsible for relations with governmental, intergovernmental and UN donors and resource mobilization. DRRM seeks to provide donors with a clear understanding of the organization’s objectives, policies, programmes and resource requirements. DRRM also liaises with field operations and headquarters units for the preparation of funding appeals, project proposals and reporting, while supporting them in their resource mobilization efforts through guidance, training and the dissemination of tools. DRRM organizes donor field missions, donor consultations and operational briefings for donors based in Geneva and capitals worldwide. It publishes the annual Global Appeal and Global Report, manages the Global Focus website, as well as producing other appeals and reports, as required.
The Private Sector Fundraising Service (PSFR), based in Copenhagen, works to raise awareness and mobilize support from private donors, including corporations, foundations, philanthropists and the general public, for UNHCR’s programmes worldwide. The Service supports fundraising operations in 27 countries in the Americas, Asia and the Pacific, Europe and the Middle East, through a network of UNHCR country offices and six national fundraising partners in Australia, Germany, Japan, Spain, Sweden and the United States. PSFR leads fundraising market development and manages the Office’s private sector fundraising growth fund, as well as international corporate and foundation partnerships. PSFR engages with corporations, foundations and philanthropists, to establish mutually beneficial partnerships, to channel additional resources to UNHCR’s core activities, and to promote innovative solutions to refugee issues. To ensure future growth and predictable revenue, PSFR develops and tests new fundraising programmes in different markets, including through digital channels, to reach large audiences and seek support for the organization’s humanitarian work.
The Records and Archives Section (RAS) is responsible for the management, preservation and access for UNHCR’s current and historical records. The implementation of e-record-keeping solutions in field offices, with the objective of enhancing accountability, knowledge transfer, efficiency, and preservation of institutional memory, is central to the Section’s work.
The Inter-Agency Coordination Service (IACS) coordinates UNHCR’s corporate positions and policies on key inter-agency humanitarian and development issues, in close consultation with respective Divisions, Bureaux and senior management. It provides guidance and support to field operations, including for refugee operations in mixed situations. The external dimension of its work includes a focus on advocating and presenting UNHCR’s positions in inter-agency fora (such as the IASC and UNDG). The IACS also works closely with DESS, in view of its role in the IASC Emergency Directors’ Group, on UNHCR’s responsibilities related to the roll-out of the Transformative Agenda.
The Governance and Partnership Service (GPS) supports the work of UNHCR’s Executive Committee (ExCom) and acts as the focal point for the Office’s relations with ExCom member States on issues of governance. It also helps facilitate bilateral relations with key UN agencies, international and intergovernmental organizations and NGOs. The Head of the Service serves as Secretary of the Executive Committee and is supported by the Secretariat and the Partnership Section. The Secretariat provides conference services for all meetings of the ExCom as well as for the High Commissioner’s Dialogue on Protection Challenges. It drafts and coordinates reports for UN governance bodies, including the General Assembly, and seeks to ensure that decisions, conclusions and resolutions of the governance bodies adequately reflect the Office’s objectives and the interests of people of concern. The Partnership Section organizes the Annual Consultations with NGOs; facilitates high-level bilateral consultations and revises MOUs with key NGO partners; supports the implementation of recommendations from the High Commissioner’s Structured Dialogue with NGOs at the field level; and facilitates the engagement of partners in the implementation of the new Refugee Coordination Model.
DIVISION OF EMERGENCY, SECURITY AND SUPPLY (DESS)
The Division of Emergency, Security and Supply (DESS) is the central support mechanism for emergency preparedness and response within UNHCR, consisting of four areas: emergency coordination, preparedness and response; security for field operations; supply and logistics; and procurement and contracting. The goal of DESS is to support the protection of people of concern through the optimal delivery of assistance in emergencies and ongoing programmes, and effective emergency response management.
The Emergency Capacity Management Service was reconfigured to the Emergency Services in 2014, and is made up of three components. The standby teams, led by principal or senior emergency coordinators, are responsible for providing emergency preparedness support to country operations, and are on permanent standby for deployment within 72 hours upon declaration of a level-2 or level-3 emergency. The Emergency Partnership and Deployment Unit strengthens UNHCR’s engagement with the extensive network of NGOs, government and civil response partners, standby partnerships and other arrangements. The Unit also strengthens UNHCR’s systems to ensure rapid deployment and that deployed staff receive appropriate support. The Emergency Policy and Capacity Development Section is responsible for ensuring that policies, guidance and training are innovative, up to date, reflect best practice and capacitate field-level delivery, with a particular focus on accountability to people of concern. It ensures that lessons learned are incorporated into emergency policy, guidance, capacity development and internal procedures, drawing on field experience, operational reviews and evaluations.
The Regional Centre for Emergency Preparedness (eCentre) is based in Bangkok, Thailand. This regional centre works with emergency management stakeholders in Governments, civil society and UN agencies throughout Asia and the Pacific to promote inter-agency preparedness in the context of humanitarian emergencies. The eCentre conducts innovative field exercises and capacity-building activities; organizes fora to facilitate structured information exchange; and provides tailored training and technical support to field operations. It also promotes strategic and operational partnerships, drawing upon its network of alumni in the region.
Many of UNHCR’s emergency operations take place in environments where the organization is exposed to various security threats. In October 2014, responding to the changed security environment, UNHCR upgraded the Field Safety Section to the Field Security Service (FSS). The decision recognized the expanded role and growing challenges of security in UNHCR’s operating environment. The mission of the Service is to strengthen UNHCR’s culture of security, based on sound risk management, allowing it to stay and deliver critical programmes in high risk contexts. Main areas of focus include: continuing to provide support and analysis to field operations; strengthening UNHCR’s security workforce through recruitment of a suitable staff and professional training; ensuring Headquarters governance and oversight of security measures; maintaining constructive engagement in inter-agency security management forums; and continuing to build staff capacity, with a particular focus on senior managers and staff members who are exposed to greater risks.
The Supply Management Logistic Service (SMLS) ensures timely and efficient delivery of relief items to people of concern, both during emergencies and for ongoing operations. In emergencies, SMLS arranges for the swift delivery of core relief items from UNHCR’s seven global stockpiles. This global stock management ensures the sustainability of the pipeline for core relief items and shelter materials. The Procurement Management and Contracting Service enhances global procurement and provide advice, guidance and training to field offices on the procurement process. The Service is responsible for services and goods procurement, quality and vendor performance management, market research, reviews and forecasting, development of supplier contracts, and management of the supply catalogue and global frame agreements. Global Fleet Management provides professional fleet management service organization-wide and is responsible for the rental, tracking, insurance and disposal of vehicles.
DIVISION OF FINANCIAL AND ADMINISTRATIVE MANAGEMENT (DFAM)
The Division of Financial and Administrative Management (DFAM) establishes and maintains the framework within which UNHCR makes optimal use of its financial resources. It is responsible for submitting UNHCR’s budget proposals to the Executive Committee and the annual statement of accounts to the UN Board of Auditors. The Division is also responsible for maintaining and improving UNHCR’s financial and management controls.
The Office of the Controller is responsible for financial policy development. The Controller directs the work of the services, sections and units of the Division.
The Policy and Audit Coordination Unit is the focal point in UNHCR for all audit matters, interacting with both the internal (OIOS) and external auditors (UN Board of Auditors), as well as the Inspector General’s Office. The Unit reviews audit findings, coordinates the organization’s responses to audit reports and prepares overviews of key audit observations and trends. It also provides expert advice and support on audit-related matters.
The Change Management and Field Support Unit supports UNHCR Field operations and Headquarters by analysing the impact of changes in financial, budgetary and administrative policies, procedures and processes. The Unit supports the implementation of corporate change initiatives, such as IPSAS, and the strengthening of financial management capacity.
The Programme Budget Service (PBS) is responsible for formulating the organization’s budget. The Service monitors the resource needs of UNHCR’s operations, providing guidance and advice on the most efficient use of resources. PBS is responsible for the development of policies, guidelines and mechanisms for budget management processes, as well as related monitoring and control in support of a sound budgetary management system.
The Accounts and Financial Service (AFS) is responsible for the production of statutory and management financial information in UNHCR.
The Implementing Partnership Management Service (IPMS) leads the development of policies, procedures, guidelines and training programmes, as well as providing support, for applying the Enhanced Framework for Implementing with Partners in the field. IPMS also ensures accountability compliance and manages the audit certifications of UNHCR-funded projects that are implemented through partners.
The Treasury Section is responsible for safeguarding cash resources, managing foreign exchange and investments and ensuring liquidity across UNHCR’s operations. It is also responsible for formulating treasury-related risk management procedures and applying best practices in global treasury management. Treasury is continuously working to improve UNHCR’s global liquidity management by using integrated treasury management systems, together with a centralized cash management approach to further enhance real-time cash positioning, increase efficiency and effectiveness in accounting and financial control.
The General Services Section is responsible for UNHCR’s building management and security at Headquarters, as well as the administration of official travel originating from Geneva.
The United Nations Board of Auditors is the external auditor for UNHCR. The Board performs a yearly audit of UNHCR’s financial statements, in conformity with the International Standards on Auditing, and expresses an audit opinion on the financial statements. The Board also undertakes a performance audit on a number of topics each year. The external audit is carried out by the National Audit Office of the United Kingdom, which was appointed as a member of the Board of Auditors for a term of six years from July 2010.
The United Nations Office of Internal Oversight Services (OIOS) provides internal audit services to UNHCR through staff based in Geneva and major UNHCR operations. OIOS conducts internal audit assignments and assists the High Commissioner in fulfilling his management functions, and acts as an oversight mechanism to ensure the proper use of UNHCR’s resources, the safeguarding of assets, the reliability and integrity of financial and operational systems and compliance with rules and regulations. The OIOS annual audit plan is prepared in consultation with UNHCR management and other oversight bodies and is based on a risk assessment of UNHCR’s operations.
DIVISION OF HUMAN RESOURCES MANAGEMENT (DHRM)
The Division of Human Resources Management (DHRM) formulates and implements human resources policies and strategies to support UNHCR and its personnel in responding rapidly to operational requirements. DHRM also upholds sound principles and practices for staff development, welfare and integrity in a service-oriented manner. In so doing, DHRM maintains global oversight of staff management across the organization. It assesses and analyses staffing profiles and emerging trends and strives to steer the organization towards sustainable human resources strategies aimed at the recruitment and retention of the most qualified and best performing staff.
The Office of the Director oversees an integrated human resources approach that is able to respond fully and strategically to operational and organizational concerns on workforce issues. Given the nature of UNHCR’s work, a primary goal for DHRM is to have a high degree of flexibility in the workforce in order to be able to ensure a quick and appropriate response according to operational needs.
HR Staff Services (HRSS) oversees functions related to personnel administration, payroll and performance management. HRSS provides HR guidance to all staff and managers worldwide; it is responsible, in particular, for ensuring that all staff members benefit from entitlements in accordance with UN staff rules; and that payroll functions efficiently at the global level in full respect of financial rules. HRSS also advises on the development of methodologies to meet HR evolving organizational needs; ensures implementation and consistent application of administrative instructions; monitors and evaluates the effectiveness of those instructions; and recommends changes. The Service includes the Personnel Administration and Payroll Section, the HQ Liaison and Compensation Unit and the Performance Management Unit.
The HR Policy and Planning Service (HRPPS) is responsible for developing human resources policies in UNHCR and ensuring quality services to HR advisory bodies. Within HRPPS a new Workforce Analysis and Business Intelligence Unit (WABI) was created to enhance UNHCR’s workforce planning and management reporting capacity; it manages data analysis systems to inform decision-making concerning the global workforce. Additionally, HRPPS provides post-classification functions for the organization. It also advocates for UNHCR positioning and interests on HR matters with partners in the UN system.
The Global Learning Centre (GLC) coordinates, designs and delivers learning activities for all staff – and to a lesser extent for UNHCR’s partners – in line with the Office’s strategic priorities. The GLC provides a wide range of diverse programmes using both distance and face-to-face methodologies to support organizational performance and career development in an efficient and cost-effective manner.
The Staff Health and Welfare Service (SHWS) is composed of the Medical Section, the Staff Welfare Section and the Global Staff Accommodation Unit. The Medical Section is responsible for monitoring, promoting and maintaining the health and safety of all UNHCR staff members. The Section ensures that staff are suitably fit to work in their locations of assignment, and delivers first aid training to prepare staff for working in emergency settings. It manages a central repository of staff medical records and is engaged in health promotion, with a focus on occupational health hazards and their prevention. The Medical Section also provides health protection to staff by monitoring and following-up on medical evacuations, and advising and counselling staff on physical or mental health issues. The Staff Welfare Section is responsible for promoting mental and psychosocial health by mitigating stress-related hazards, especially in field operations with high-security challenges and hardship living conditions. Counsellors provide trauma interventions and support the implementation of preventive procedures such as pre- and post-deployment psychological debriefings. The Global Staff Accommodation Unit is responsible for supporting field operations in meeting UNHCR minimum standards of working and living conditions for all UNHCR staff worldwide, contributing to the SHWS’ mandate to enhance staff health and welfare. The Unit also pioneers innovative, environmentally-sensitive and durable accommodation solutions.
The Assignment and Career Management Service (ACMS) is composed of the Career Management Support Section (CMSS) and the Assignments and Promotion Section (APS).
Through facilitating effective linkages between posting, career management and training, CMSS provides individual career counselling to staff members and career development opportunities in collaboration with the Global Learning Centre. CMSS regularly delivers career-support activities to field-based staff through career planning or career transition workshops adapted to specific country operations.
APS plays an integral role in the assignments process for all positions. In conjunction with CMSS, APS consults with staff and managers to match applicants to vacant positions. APS also assumes secretariat functions for the matching process, the Joint Review Board, and provides full oversight of all assignments. In addition, it serves as the secretariat for the yearly promotions sessions, including providing associated help-desk functions.
A Strategic and Transformative HR Service (STHRS) has been created in DHRM comprising of the Talent Outreach and Acquisition Section (TOAS) in Budapest and a new Geneva-based Strategic HR Unit.
TOAS was established in 2014 to implement UNHCR’s strategies related to the outreach and acquisition of talent. The Section works to attract external talent to the organisation through four major recruitment programmes: the Entry-Level Humanitarian Professional Programme (EHP); the Capacity Building Initiative (CBI); Profile-Based Recruitment; and ad-hoc recruitment to attract high-level leadership and specialized talent in specific functional areas. TOAS also acts as the focal point and business partner coordinator for UNHCR’s programmes with UN Volunteers (UNV), the United Nations Office for Project Services (UNOPS), Junior Professional Officers (JPOs), consultants and contractors; and provides all the necessary recruitment indicators to guide the management of recruitment processes in line with UNHCR’s strategic objectives.
The key objective of the new Strategic HR Unit, created in 2015, is to address evolving organizational human resources challenges through the implementation of an HR strategy, as well as through enhanced partnerships with divisions and bureaux, leadership and talent management, and coordination of all HR aspects of emergency preparedness and response.
DIVISION OF INTERNATIONAL PROTECTION (DIP)
The Division of International Protection (DIP) develops global protection policy, contributes to standard-setting and progressive development of international law and standards in the area of forced displacement and statelessness, provides guidance on complex international law and protection policy issues pertaining to all categories of populations of concern and to UNHCR’s field operations, leads the age, gender and diversity approach, and provides support to field operations and other headquarters’ entities on protection policy, legal and operational matters relating to forced displacement and statelessness, including status determination and related issues, from both protection and durable solutions perspectives.
The Office of the Director provides leadership to the Division with regard to legal issues and policy formulation, as well as support to field operations. It guides headquarters Divisions and Bureaux and field operations on global protection issues, particularly in the context of protection strategy formulation and support in emergencies.
The division is organized in a series of sections and units.
The Protection Policy and Legal Advice (PPLA) Section’s mission is to advance international legal standards on the protection of asylum-seekers and refugees, and to provide thematic doctrinal advice and guidance to governments and field operations.
The Asylum/Migration Unit ensures UNHCR’s engagement in international migration issues as they relate to forced displacement and statelessness. The Unit supports the regional Bureaux and field offices in advocating for protection-sensitive, comprehensive regional approaches to mixed migratory movements. The Unit also supports UNHCR’s engagement in global migration processes, including the Global Forum on Migration and Development and the Global Migration Group.
The Human Rights Liaison Unit engages with the human rights mechanisms of the United Nations and other bodies to strengthen the international legal framework on people of concern to UNHCR, and to mainstream and promote effective use of human rights norms as both advocacy and complementary protection tools for persons of the Office’s concern.
The Statelessness Section develops doctrine and tools on statelessness and provides support to field operations and external actors, in furtherance of UNHCR’s statelessness mandate. The Section promotes implementation of the Global Action Plan to end statelessness by 2024 – including through support to UNHCR field offices, provision of technical advice for nationality law and policy reforms, and regional and country-level meetings with governments to exchange best practices in addressing statelessness.
The Refugee Status Determination Section is responsible for developing and implementing UNHCR RSD and RSD-related strategies, as an integral part of UNHCR’s broader protection and solutions strategies. The Section aims to strengthen international refugee protection by enhancing the quality and efficiency of UNHCR and State RSD procedures, including in emergency and other special operations. The Section provides support through training, legal and procedural advice, expert missions and deployments. It also issues country-specific guidance documents to assist UNHCR staff and state decision-makers in individual asylum procedures, and works intensively with States and intra-state organizations to ensure that country of origin information (COI) available to decision-makers in different jurisdictions is of the highest possible quality.
The Protection and National Security Unit leads efforts to ensure that measures to counter terrorism and other threats to national or international security comply with international legal obligations towards people of concern to UNHCR. The Unit also monitors legal and policy developments in the area of exclusion from international refugee protection. It provides guidance and advice on legal and policy issues, including through individual case review, as well as training on exclusion, extradition and national security issues for UNHCR staff and government officials in regions dealing with complex caseloads.
The Resettlement Service advances UNHCR’s global resettlement agenda by promoting resettlement as an integral component of comprehensive protection and solutions strategies, and ensuring that durable solutions are applied in a complementary manner to maximize solutions opportunities for a higher number of refugees. The Resettlement Service also revises relevant guidelines, including those addressing fraud committed by refugees, and participates in multi-functional technical anti-fraud assessment missions to provide support and advice to UNHCR operations dealing with resettlement priority situations.
The Community-Based Protection Unit focuses on enhancing UNHCR’s organizational capacity to deliver community-based protection through the issuance of guidance, including targeted support to country operations. The Unit promotes good practices and develops global training packages, for example in the areas of disability inclusion and protection of LGBTI people of concern, while continuing to pursue the multi-year transition of the community services function to community-based protection.
The Child Protection Unit continues to roll out the Framework for the Protection of Children, launched in 2012, and provides operational and technical support in the development of multi-year country-level child protection strategies. The Unit responds to the critical needs of unaccompanied children and other children at risk of secondary movement, and smuggling and trafficking. The Unit also has a strong focus on adolescents and youth, supports specific projects for through the Youth Initiative Fund, and engages in advocacy and awareness-raising.
The Sexual and Gender-Based Violence (SGBV) Unit provides technical guidance and operational support on SGBV prevention and response, develops training tools and builds partnerships to strengthen UNHCR’s protection work in this area, in close collaboration with the senior regional protection officers and a network of six emergency staff with dedicated SGBV responsibilities.
The Gender Equality Unit works to incorporate the Age, Gender and Diversity (AGD) Accountability Framework into UNHCR’s online planning and reporting system. Through the Unit, UNHCR remains an active member of the GenCap Steering Committee.
With a strong focus on monitoring, the Education Unit assists over 25 field operations to implement country-specific education strategies aimed at increasing access to quality education and strengthening accelerated education programmes in collaboration with a network of education agencies. Given the role of education in supporting durable solutions, the Unit advances the goal of integrating children of concern in national education systems through strengthening a broad partnership base with Ministries of Education and other education actors.
The Protection Support Unit provides protection support for both refugee and IDP emergencies, and for ongoing operations in coordination with regional Bureaux, supports Divisions at headquarters and field operations. Specific support includes staffing and deployment capacity for protection, guidance on protection strategies, protection information management, and the development of tools for protection in emergencies.
The Internally Displaced Persons Section guides UNHCR’s engagement in IDPs situations through policy and operational support, coordination of protection clusters and support to ensure the centrality of protection in emergencies. It supports an enhanced institutional response to IDP situations in the field, while promoting effective advocacy on globally relevant protection issues. The Section aims to strengthen UNHCR’s institutional response in protection and assistance in situations of internal displacement. It guides UNHCR’s operational engagement through planning processes with field operations, regional Bureaux and support Divisions at headquarters, while providing targeted and timely responses during emergencies. In cooperation with the Special Rapporteur on the Human Rights of Internally Displaced Persons, IDMC, The Brookings Institution, OHCHR, OCHA and other partners, the IDP Unit facilitates consultation and training on the Guiding Principles on Internal Displacement, and promotes development of normative frameworks for internal displacement, which includes support for the ratification and implementation of the AU’s Kampala IDP Convention.
The Global Protection Cluster (GPC) Support Cell supports the UNHCR’s leadership and coordination functions and the GPC’s broad membership and provides inter-agency policy advice and guidance on protection and implementation of the cluster approach in 33 clusters and other protection coordination mechanisms worldwide. The GPC aims to strengthen support for field operations and enhance global engagement on protection in internal displacement. Issues requiring strategic planning and advocacy are addressed through the coordinated efforts of the GPC Support Cell, the GPC Areas of Responsibility (AORs), and strengthened collaboration with key operational UN agencies and international NGOs in the area of protection.
Situated within DIP is also the Comprehensive Solutions Unit, which, in collaboration with the Solutions Steering Group, as well as with other parts of DIP, supports regional Bureaux and field offices in in the design, development and implementation of comprehensive protection and solutions strategies. The Unit develops and tests guidance materials and provides technical advice on the more operational aspects of protection is this relates to solutions including: context mapping; voluntary repatriation, including intention surveys; protection-sensitive migration opportunities; cessation processes; the right to dignified work; housing, land and property; and access to justice.
Finally, the Resource Management Unit facilitates operational activities by providing human resources, financial and administrative support to DIP.
The sections and units within the Division collaborate to meet the needs of field offices and the Organization for timely and effective policy, legal, and operational guidance and advice in the field of protection.
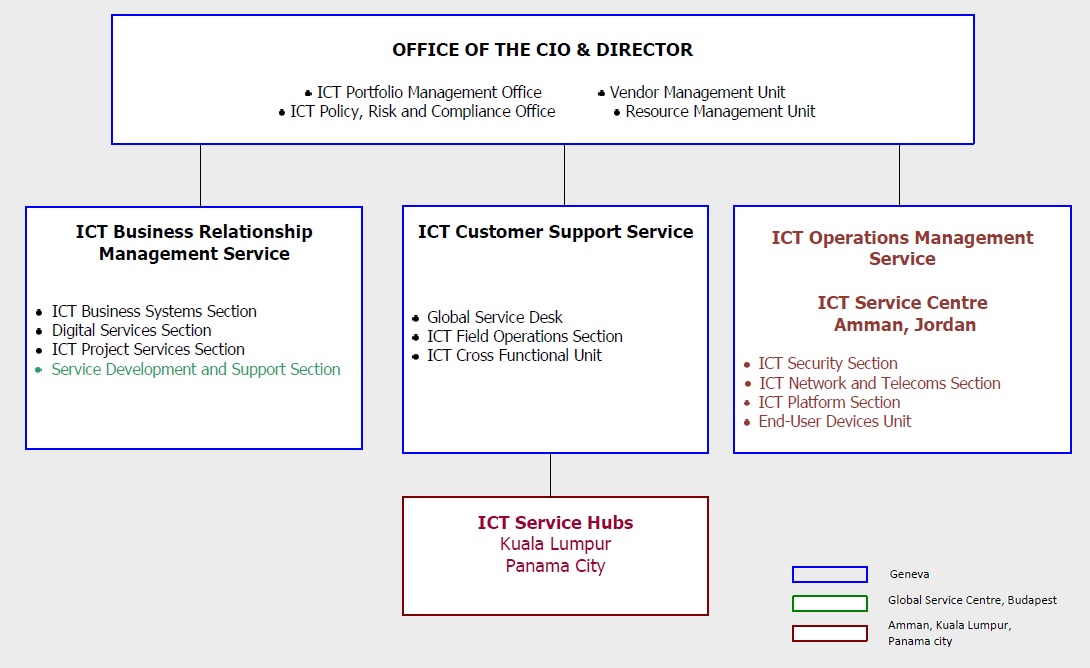
DIVISION OF INFORMATION SYSTEMS AND TELECOMMUNICATIONS (DIST)
The Division of Information Systems and Telecommunications (DIST) is responsible for ensuring that UNHCR takes advantage of cost effective information and communications solutions that enable and facilitate UNHCR’s execution of its mandate.
Led by the Chief Information Officer and Director of DIST, the Office of the Director is responsible for providing leadership and support in information technology for UNHCR worldwide. The CIO is responsible for technology strategy and planning, performance and results, policy formulation, investment planning and oversight, compliance and audit coordination, supplier relationship management, and resource management.
The Vendor Management Unit maintains a direct relationship with external vendors which provide services to the organization and oversees the contractual aspects of vendor management.
The ICT Portfolio Management Office maintains the portfolio of all ICT projects and programmes and ensures that the UNHCR standard project methodology is followed and that project reviews are completed throughout the development lifecycle.
The Policy, Risk and Compliance Office is responsible for developing and maintaining the catalogue of ICT Policies and Guidelines, conducts regular risk analysis and compliance reviews on the existing ICT systems.
The Business Relationship Management Service works to improve UNHCR’s operations in the Field and in Headquarters by ensuring that the services provided by DIST are fit for purpose and is responsible for the day to day running of UNHCR’s portfolio of refugee related software systems.
The ICT Project Services Section is responsible for the execution of projects according to the Project Management Life Cycle. It develops, maintains and tracks project plans and schedules, cost estimates, risk and problem logs, and ensures that each project remains on schedule and on budget.
The Service Development and Support Section is directly responsible for the delivery of new applications, enhancements to existing applications, and business as usual or ongoing support.
The Business Relationship Management Team provides focal points for all Divisions and Bureaux, as well as specific leads for critical application areas in order to support operations.
The Customer Support Service has overall responsibility for the provision of quality services to the UNHCR user community. Within the service, the Global Service Desk is responsible for registering and ensuring the resolution of all ICT incidents and service requests across the organization.
The ICT Field Operations Section is responsible for providing global on-site ICT support services and also ensures that DIST has in place the structure, processes, resources and capacity for emergency preparedness and response. This section takes the lead in ensuring that the emergency operation has adequate ICT resources (equipment and staff) and deploys short-term ICT staff resources.
The ICT Cross Functional Unit is responsible for a series of functions that straddle the three DIST services. These include change management, asset management, and configuration management. It ensures that ICT projects are integrated into the business processes and services; errors are reduced and risks minimized from transition to production systems; and that services can be used as per requirements.
The ICT Operations Service has overall responsibility to deliver and maintain the common ICT Infrastructure which is the foundation of all services provided by DIST. Within the service, the ICT Security Section is responsible for developing policies and standards in relation to ICT security in both applications and infrastructure and ensuring compliance.
The ICT Network and Telecoms Section is responsible for the overall delivery of Local and Wide Area Network services and long-term network and telecommunications strategy of DIST to increase efficiency of the network and extend its reach to the final point of delivery in deep-field locations.
The ICT Platform Section is responsible for the overall delivery of UNHCR’s Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS) and for the medium and long-term Platform strategy of DIST to ensure efficient delivery of platform and applications, with emphasis on those located in deep-field locations.
The End-User Devices Unit is responsible for the overall delivery of UNHCR’s End-User Devices configuration and support infrastructure, including computers and mobile devices, in Headquarters and the Field, to ensure efficient delivery of corporate applications and end-user services through appropriately identified and configured workstation and mobile devices. It also defines common standards for these devices, working with the Infrastructure Managed Service Provider in the implementation and compliance validation of these standards.
DIVISION OF PROGRAMME SUPPORT AND MANAGEMENT (DPSM)
The Division of Programme Support and Management (DPSM) works to provide the knowledge, guidance and tools necessary to design and deliver UNHCR programmes that demonstrate quality, technical integrity and innovation. The Division leads efforts to strengthen results-based management (RBM) within UNHCR and to ensure that planning, implementation and key management decisions are based on evidence and sound analysis. DPSM sets strategies, policies and standards and develops practical guidance and tools across a wide range of technical areas, from public health to food security and nutrition, water sanitation and hygiene, shelter and settlements, solutions, livelihoods and self-reliance, domestic energy, environmental management, registration, information management and statistics.
DPSM directly supports field operations through the deployment of experts and through global technical specialist networks, placing the highest priority on responding rapidly and effectively in emergencies. The concept of protection guides all dimensions of the Division’s work, which is supported through collaboration and strong partnerships with all of UNHCR’s key partners. DPSM manages its diverse and challenging agenda through two pillars, covering a) programme and operational data management; and b) technical support.
The Programme Analysis and Support Section (PASS) provides guidance on programme planning, implementation, monitoring and analysis. The Field Information and Coordination Section (FICSS) leads operational data management, focusing on registration and biometrics, information management, GIS and mapping technologies, statistics, surveys and profiling, and needs assessments. The Section also co-leads the Global CCCM Cluster alongside IOM.
The Public Health Section (PHS) oversees UNHCR’s programmes in public health, HIV and reproductive health, nutrition and food security, and water, sanitation and hygiene (WASH).
The Operational Solutions and Transition Section (OSTS) promotes solutions for refugees and the strengthening of key linkages with development actors. The Division plays a key role in the Solutions Steering Group in bringing greater focus and coherence to UNHCR’s work in this area and also significantly strengthened technical support to field operations. The Section also supports energy and environment interventions and livelihood programmes that build up refugees’ self-reliance.
The Shelter and Settlement Section (SSS) provides technical support for the development of global and country-level shelter strategies and planning. Through research and development, the Section offers field operations improved shelter solutions and site planning options. It also co-leads the Global Shelter Cluster in partnership with the IFRC.
Established in 2014, the Cash-Based Interventions Section (CBIS) provides overall coordination and guidance of CBIs and is supporting field operations with improved methodologies and tools for coordinated needs assessments, programme design, monitoring and communicating with refugees and other affected populations.